Introduction
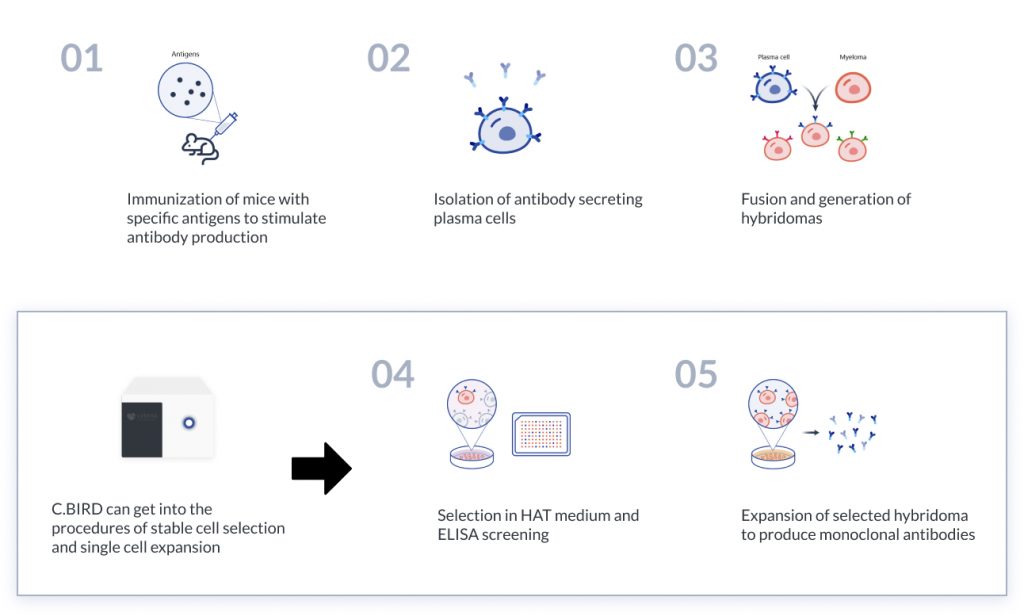
Hybridoma is the fused cell of primary B cell and myeloma cell which produce specific and identical antibodies for an unique epitope. The stable hybridoma has both capabilities of immortalization and monoclonal antibody producing, which is widely used for laboratory immunoassay or immunodiagnosis.
The mammals such as mice or rabbit, are injected with an antigen to induce an immune response. The antibody producing B cells are then isolated from the mammals to fuse with myeloma cell as a hybrid cell line called hybridoma. The mixture of hybridomas are necessary to separate single cell to ensure monoclonality, and then expand to a larger scale over several weeks.
Introduction
Hybridoma is the fused cell of primary B cell and myeloma cell which produce specific and identical antibodies for an unique epitope. The stable hybridoma has both capabilities of immortalization and monoclonal antibody producing, which is widely used for laboratory immunoassay or immunodiagnosis.
The mammals such as mice or rabbit, are injected with an antigen to induce an immune response. The antibody producing B cells are then isolated from the mammals to fuse with myeloma cell as a hybrid cell line called hybridoma. The mixture of hybridomas are necessary to separate single cell to ensure monoclonality, and then expand to a larger scale over several weeks.

To accelerate the cell culture timeline
Performance data
An Innovative Cell Culture Method for Hybridoma in Early Stages
CHO-K1 mAb expressing cell line was used for the study. The cell line was adapted to suspension culture in a chemically defined and animal-component-free medium (CD Hybridoma medium #11279-023 by GibCo). Standard 96-well plates (Eppendorf #0030730011, Germany) were used for all experiments.
Comparison studies were performed with cells cultivated in standard static culture, 30 mL shaker-flask culture (shaking speed: 130 rpm; orbit:19 mm) and C.BIRD suspension culture in a 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator environment.


Figure 2. The cell growth and antibody production of three culture methods in 7 days of continuous culture. he C.BIRD facilitated the cell growth in both A) total cell density and B) viable cell density while maintaining the same C) viability as the other two groups. In addition, the C.BIRD group showed a significantly higher D) antibody production at Day 7 compared to both static and shaker-flask groups.



